To efficiently design and develop an app, we must simultaneously use strategies that guarantee success, and think about the support in itself: the smartphone. In 2022, almost 2023, it goes without saying that we insist more on the ‘smart’ aspect than the ‘phone’ aspect. Indeed, features are so advanced that we truly hold little technological marvels in our hands. We must consider all the features offered on a phone to create a complete, intuitive, and inventive app. Discover the list of features to mobilize when developing a mobile app
The Smartphone’s Physical Features
First, let’s talk about the physical features we find on a phone; in other words, the features that will work with your senses to prolong interaction. Whether it be through sight, touch, or hearing, we must carefully solicit them to create a complete experience in every type of app.
1. Touch Screen
The multi-touch screen absolutely needs to be leveraged to make intuitive and fluid experiences. The taps, swipes, pinch, and gestures dramatically add to the experience when included properly. On the same note, think about an app’s quick action items (long press on the app icon): this feature, quite frequently overlooked, but not hard to implement, adds to the polish of an app and promotes usability.
2. Haptic Feedback
Hirokazu Tanaka, Nintendo sound effects developer in the 80s, said: “Even if just a beep, sound is important in games; you need sound to confirm action; otherwise, you wouldn’t know what you were doing”. Haptic feedback is a way for an app to communicate information to the user through touch, as it makes the device vibrate in a variation of ways. Nowadays, this feature is well known by smart watch users as they receive multiple notification types throughout the day.
3. Camera
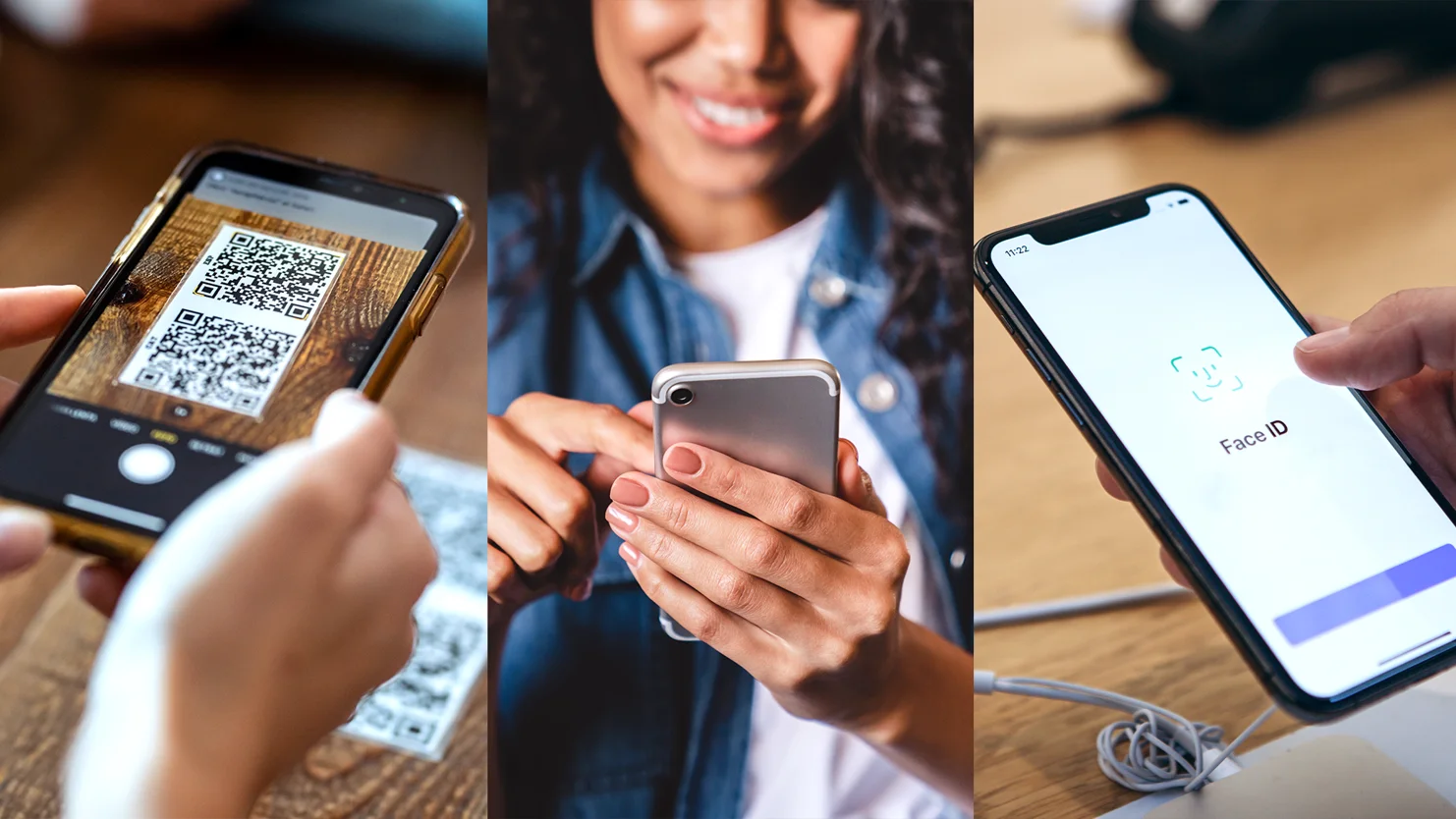
As a key feature in any phone, the camera will allow the user to take pictures and videos – obviously – but also to scan documents, barcodes, 2D codes (like QR codes) or even run live translations. Many apps leverage these features to submit paper documents or to facilitate the product search through barcode reading or image recognition application programming interfaces (APIs). The camera can also be used to create 3D models of spaces.
4. Biometric Sensor or Facial Recognition
Now available on most devices, these features act as an authentication proxy to facilitate user logins. They should really be part of either the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) or fast-follow updating features, as these produce a high-convenience level for the users.

Relationship Functionalities in a Smartphone
It’s one of the reasons we use our phones daily: connecting with others, interacting, and keeping ourselves informed of what’s going on. These features can be used in a series of apps dedicated to relations – whether they be for clients, business partners, or employees.
5. Messaging
Messaging has always been at the core of the digital usage growth and client relationship apps. Indeed, this feature conveys the human accessibility that most users are looking for when trying to solve an issue, to get information or to require help in an emotionally sensitive context.
6. Notifications
Notifications are an essential part of any messaging app, but they also represent a good way to inform users on key elements worthy to know.
Geolocated push notifications present interesting use cases, especially in customer relationship apps: you can greet a customer upon entry of a store and let them know of any key information for the day (activities, promotions). Notifications – when used properly – will create more app engagement; there is a fine line between usefulness and annoyance.
Notifications have gotten more and more sophisticated with the years. iOS and Android now offer rich notifications, i.e. notifications with images and micro actions. A micro action example could be replying to a message from the notification itself, adding a layer of convenience. Furthermore, on Android, it is possible to add constant notifications to make sure your navigation instructions are displayed on top of the notification centre when Google Maps is active.

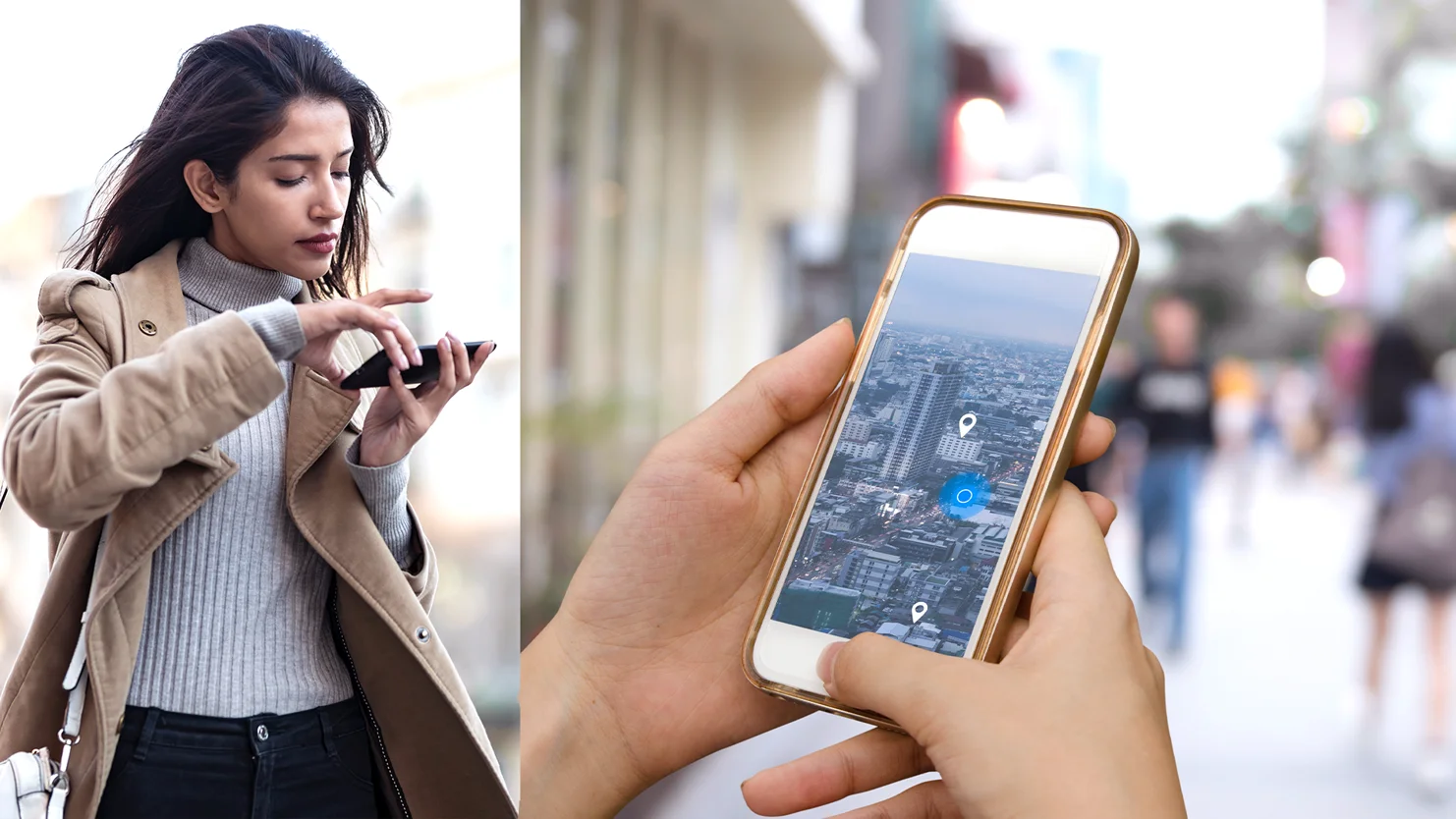
The Smartphone’s Spatial Features
Another fundamental capacity of the phone: it can locate itself in any space. This is very interesting for several apps, including apps that concern movement or apps that require to interact with the environment or other content.
7. Gyroscope and Accelerometer
Without these sensors, many frequently used apps would not work. The gyroscope enables finding the phone’s orientation, but also categorizing our movements. In addition, the accelerometer can detect movement.
8. GPS
The GPS feature is relevant in several geolocation use cases. It helps to locate the user on a map, it increases EXIF (Exchangeable image file format) data in camera apps, it calculates speed in navigation apps (Waze), or it provides geolocated content either in-app or when coupled to notification services.
9. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
These experiences often apply to knowledge-sharing and training contexts where people can practise different skills, learn procedures and processes, visualize working environments, or plan for manufacturing reorganization. Exposure to AR is a little more common in most people’s day-to-day lives and offers the possibility to overlay content on a scene by recognizing a marker or an image. This is a feature we recently implemented in the Insectarium app.

Connectivity Features in a Smartphone
Smartphones offer several options that allow apps to be useful and differentiating. These features are used in many app types, including brand apps and apps connected to extensions.
10. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
Bluetooth, which is mostly used in two use cases, i.e. geolocation and Internet of Things connectivity (speakers, thermostats, heart rate straps, tennis rackets, cars, manufacturing machines), provides lots of benefits to an app when connection is needed. Wi-Fi is useful to connect to IoT devices like printers or GoPro-type cameras, but also for tracking and analytics purposes.
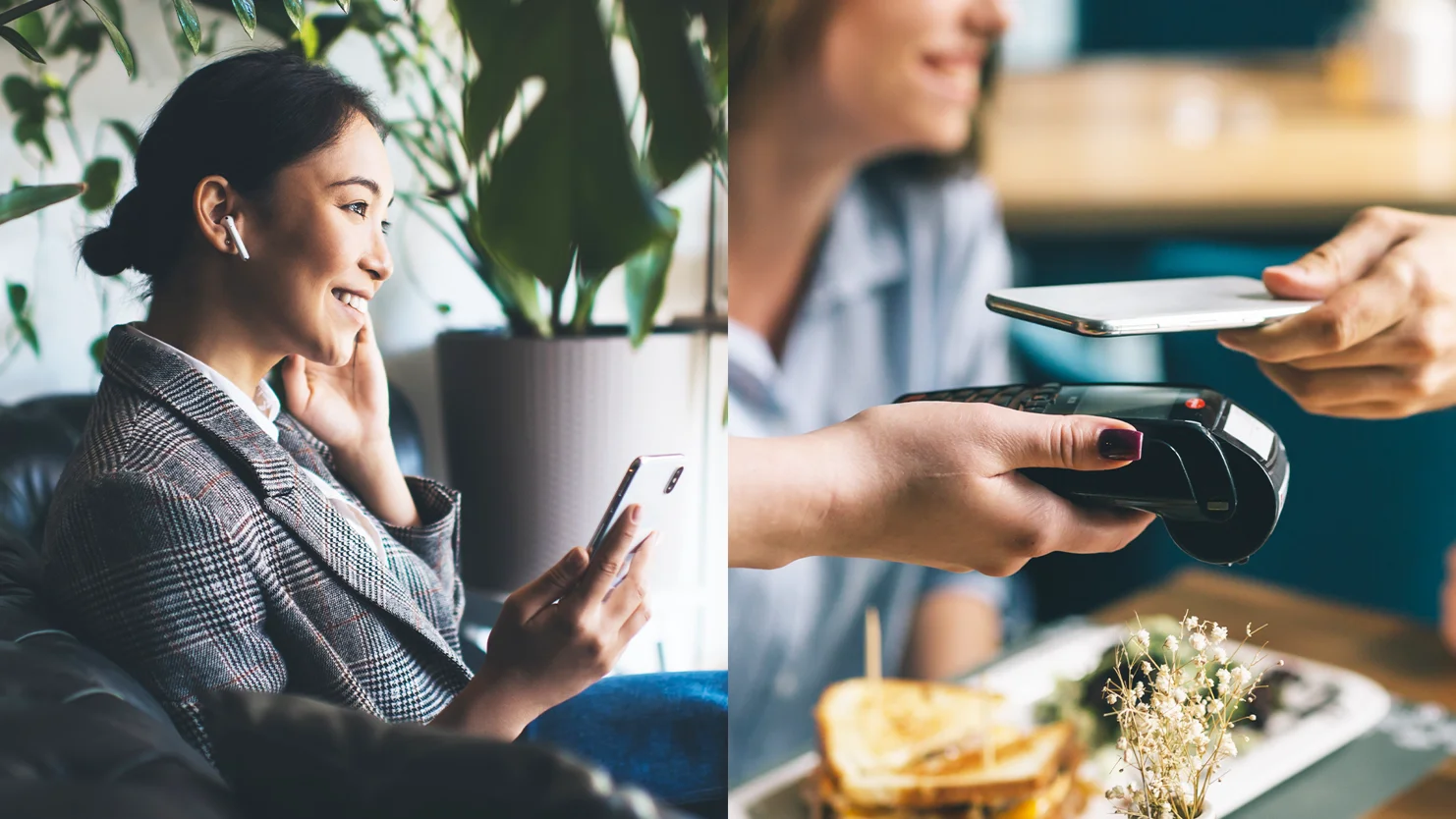
11. Payment
Micro transactions have been key in the early years of the mobile era to generate revenue in the business-to-customer (B2C) marketplaces. As payment solutions evolved, this feature became more and more optimized in recent years.
12. Offline Storage
Data connectivity isn’t offered in all areas and sometimes can be unavailable. Thorough app use cases consider maximizing the devices’ storage capabilities to download content in advance or to store data offline to synchronize later.
Using Features to Improve a Mobile App’s Usability
As an innovator, optimizing dynamic interactions for mobile positions in an app is a fun process, but more importantly, it should create further engagement and usability. An app will be considered easy to use if it contributes to effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction. Technology can contribute to these qualities by preventively sending relevant notifications, facilitating the conclusion of a transaction, adding 3D models that will help us make more informed decisions, etc. From a technology-design perspective, features should be considered in the context in which they will be used, with a specific user goal in mind.
When we take the time to dive deeply into these contexts prior to the development stage, the possibilities become endless. Then we can really innovate.

Featured articles
Technical or financial, debt becomes expensive when left to accumulate. But when managed properly, technical debt can become a driver of efficiency. Through regular maintenance,…